Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

The Nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell.
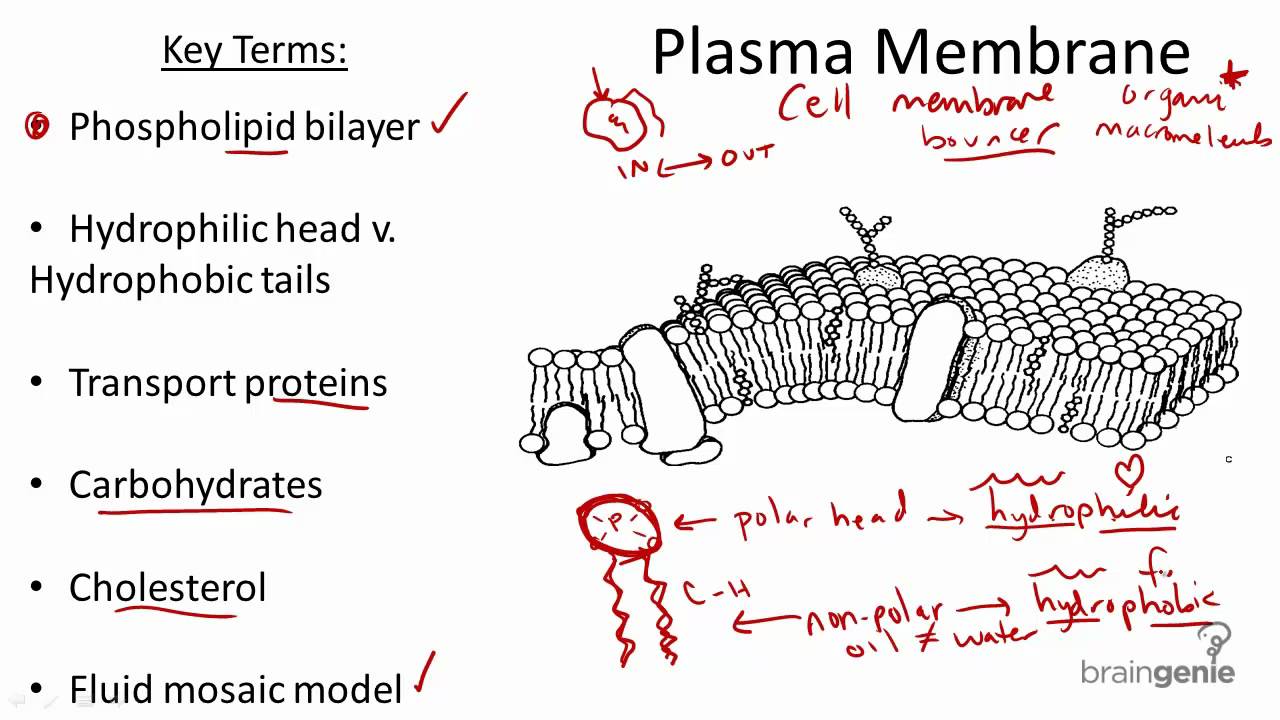
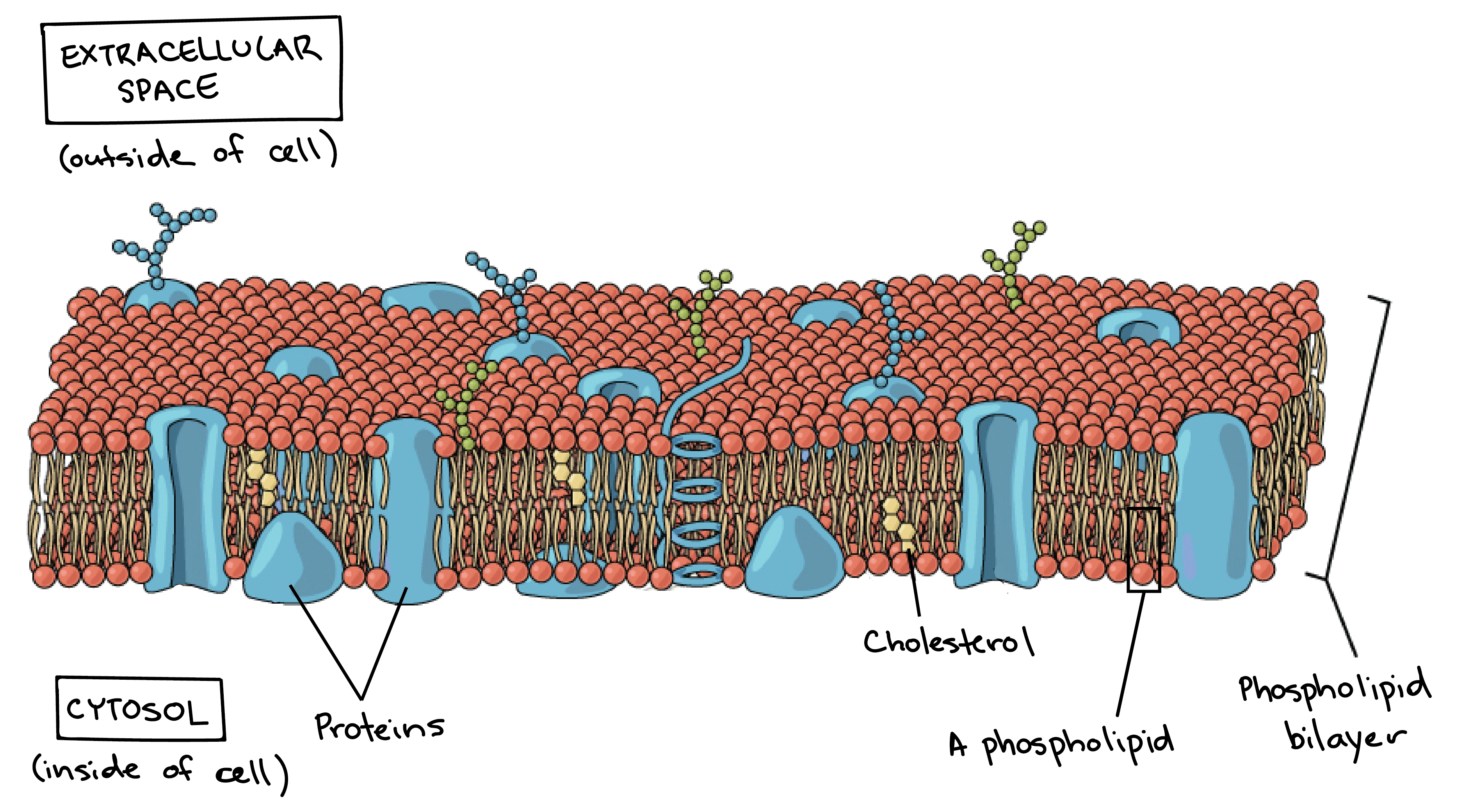
Cell membrane structure and function a level. This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. Different organelles have distinct structures and functions. Some of these proteins span the whole width of the membrane.
The membrane is examined in detail later. Membranes also exist within cells forming various. Thin barrier separating inside of cell cytoplasm from outside environment Function.
Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane. The membrane also contains membrane proteins including integral proteins that go across the membrane serving as membrane. The nucleus is surrounded by nuclear envelope pair of membranes.
Act as a barrier to most water-soluble substances the non-polar fatty acid tails prevent polar molecules or ions from passing across the membrane. Formed from a phospholipid bilayer with the hydrophobic tails pointing towards each. The separation of different parts of the cell with different functions by using membranes is called compartmentalisation providing distinct conditions for different processes.
Both the cell surface membrane and the membranes surrounding certain organelles have the same basic structure. It separates the contents of the cell from the outside environment and controls the entry and exit of materials. Many membranes within the cell help to make different compartments for different chemical reactions to take place.
Functions of membrane systems and organelles. Cell Membranes a outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells b state that plasma cell surface membranes are partially permeable barriers Plasma membranes are partially permeable meaning they let some molecules through but not others. The liquid where all.