Cellular Respiration Formula With States

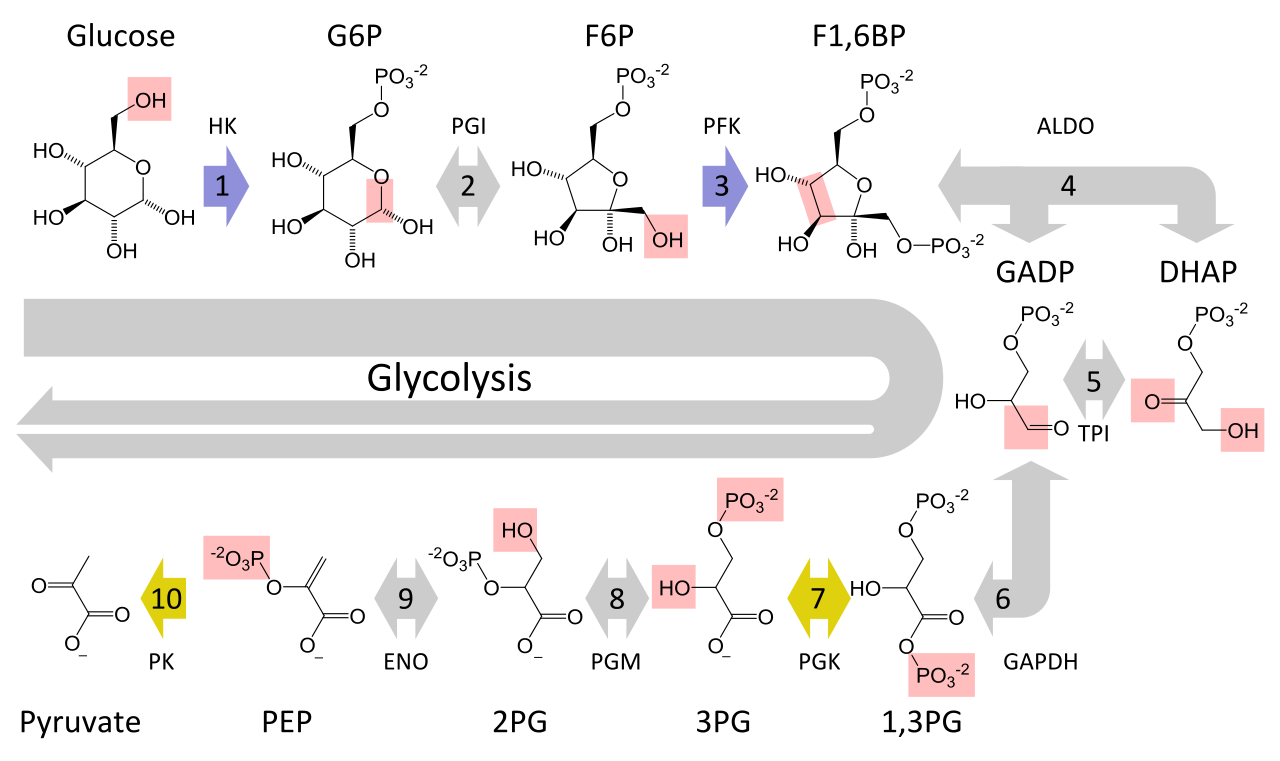
The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
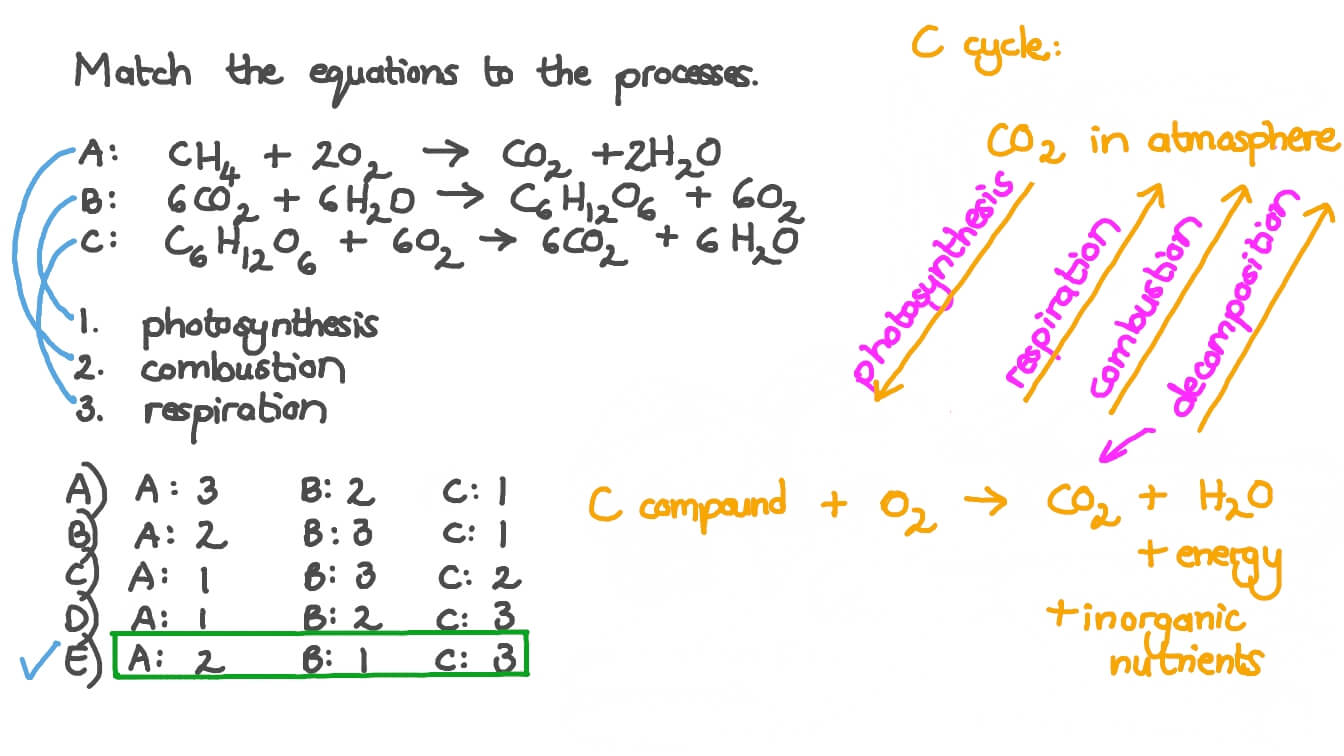
Cellular respiration formula with states. Glucose 6 oxygen 6 carbon dioxide 6 water ATP. Explain why aerobic cellular respiration results in 36 ATPs per glucose in eukaryotic cells and 38 ATPs per glucose in prokaryotic cells. This is a balanced equation of the cellular respiration of glucose.
Glucose Oxygen Carbon Dioxide water energy Heres an article on it. A glucose molecule combines with 6 oxygen molecules producing 6 molecules of water 6 molecules of water and ATP. To unlock this lesson you must be a.
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms convert the biochemical energy of nutrients into ATP. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Glucose Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water ATP C 6H 12O.
The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 -- 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O ATP is the complete balanced chemical formula for cellular respiration. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is C6H1206 6O2 6CO2 6H2O energy ATP.
Redox describes all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed. However cellular or aerobic respiration takes place in stages including glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. The overall chemical equation for aerobic respiration is C6H12O6 6O2 6H2O 12H2O 6CO2 3638ATP.
Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and electron transportoxidative phosphorylation. The overall unbalanced chemical equation for cellular respiration is. There are three main stages of cellular respiration.