Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Signal transduction The transmission of signals from a cells outside to its inside. Cellular respiration stores chemical energy in the form of phosphorylated nucleotides primarily ATP by means of oxidative reactions and makes it available to other reactions. In contrast to simple combustion cellular respiration involves the step-wise release of energy in a tightly regulated fashion.
Cellular respiration Energy from nutrients is converted into ATP. Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy.
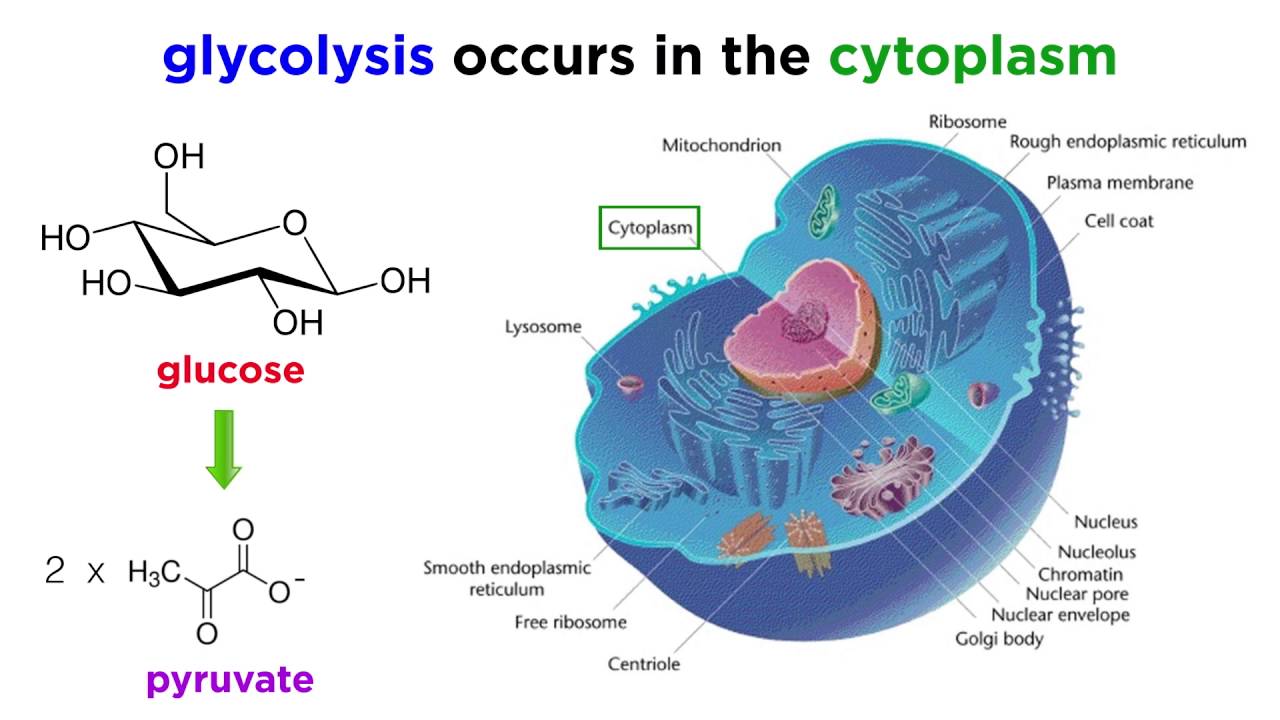
In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell. ATP for use in energy-requiring activities of the cell.
In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. Anaerobic respiration is another type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen and produces energy. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule.
Cellular respiration the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding as waste products carbon dioxide and water. In this process glucose is broken down in the presence of molecular oxygen into six molecules of carbon dioxide and much of the energy released is preserved by turning ADP and free phosphate into ATP. Cellular respiration can be described as the reverse or opposite of photosynthesis.
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate ATP. Hydrolysis Breaking a bond in a molecule and splitting it into smaller molecules through a reaction with water. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products.